​an Excess of Vitamin _____ Can Result in Hardening of Blood Vessels Due to Excess Blood Calcium.
A Harvard Health article
Vitamins and Minerals
Are Y'all Getting What You Need?

Vitamins and minerals are essential nutrients because they perform hundreds of roles in the trunk. At that place is a fine line between getting enough of these nutrients (which is healthy) and getting too much (which tin end upwardly harming you). Eating a healthy diet remains the best fashion to get sufficient amounts of the vitamins and minerals yous demand.
Essential nutrients for your trunk
Every mean solar day, your body produces skin, muscle, and bone. It churns out rich cherry-red blood that carries nutrients and oxygen to remote outposts, and it sends nerve signals skipping along thousands of miles of brain and body pathways. It besides formulates chemical messengers that shuttle from 1 organ to another, issuing the instructions that help sustain your life.
But to do all this, your trunk requires some raw materials. These include at least thirty vitamins, minerals, and dietary components that your trunk needs but cannot industry on its ain in sufficient amounts.
Vitamins and minerals are considered essential nutrients—because acting in concert, they perform hundreds of roles in the body. They help shore up bones, heal wounds, and eternalize your immune arrangement. They likewise catechumen food into free energy, and repair cellular damage.
But trying to keep track of what all these vitamins and minerals do tin exist confusing. Read enough articles on the topic, and your optics may swim with the alphabet-soup references to these nutrients, which are known mainly be their initials (such as vitamins A, B, C, D, E, and K—to name merely a few).
In this article, you'll gain a better understanding of what these vitamins and minerals actually do in the body and why y'all want to brand sure you're getting enough of them.
Micronutrients with a large role in the body
Vitamins and minerals are often called micronutrients considering your body needs only tiny amounts of them. Still declining to get even those small quantities virtually guarantees disease. Here are a few examples of diseases that tin result from vitamin deficiencies:
- Scurvy. Old-time sailors learned that living for months without fresh fruits or vegetables—the main sources of vitamin C—causes the haemorrhage gums and listlessness of scurvy.
- Blindness. In some developing countries, people still get blind from vitamin A deficiency.
- Rickets. A deficiency in vitamin D can cause rickets, a condition marked past soft, weak basic that can atomic number 82 to skeletal deformities such as bowed legs. Partly to combat rickets, the U.S. has fortified milk with vitamin D since the 1930s.
Just as a lack of key micronutrients can cause substantial harm to your body, getting sufficient quantities can provide a substantial benefit. Some examples of these benefits:
- Strong bones. A combination of calcium, vitamin D, vitamin M, magnesium, and phosphorus protects your basic against fractures.
- Prevents nativity defects. Taking folic acid supplements early in pregnancy helps foreclose encephalon and spinal birth defects in offspring.
- Good for you teeth. The mineral fluoride not only helps bone formation simply also keeps dental cavities from starting or worsening.
The difference between vitamins and minerals
Although they are all considered micronutrients, vitamins and minerals differ in basic ways. Vitamins are organic and tin can be cleaved down past estrus, air, or acrid. Minerals are inorganic and agree on to their chemical construction.
So why does this matter? It means the minerals in soil and water easily find their way into your body through the plants, fish, animals, and fluids you swallow. But it's tougher to shuttle vitamins from food and other sources into your torso considering cooking, storage, and elementary exposure to air can inactivate these more than fragile compounds.
Interacting—in good means and bad
Many micronutrients interact. Vitamin D enables your trunk to pluck calcium from nutrient sources passing through your digestive tract rather than harvesting it from your bones. Vitamin C helps you absorb iron.
The coaction of micronutrients isn't always cooperative, all the same. For case, vitamin C blocks your body's power to digest the essential mineral copper. And fifty-fifty a pocket-sized overload of the mineral manganese tin worsen atomic number 26 deficiency.
Affordable Online Therapy
Get professional help from BetterHelp's network of licensed therapists.
HelpGuide is reader supported. We may receive a commission if you sign upward for BetterHelp through the provided link. Learn more than.
A closer expect at water-soluble vitamins
Water-soluble vitamins are packed into the watery portions of the foods you consume. They are absorbed direct into the bloodstream every bit food is broken downward during digestion or every bit a supplement dissolves.
Because much of your body consists of water, many of the h2o-soluble vitamins circulate easily in your trunk. Your kidneys continuously regulate levels of water-soluble vitamins, shunting excesses out of the trunk in your urine.
Water-soluble vitamins
B vitamins
- Biotin (vitamin B7)
- Folic acrid (folate, vitamin B9)
- Niacin (vitamin B3)
- Pantothenic acid (vitamin B5
- Riboflavin (vitamin B2)
- Thiamin (vitamin B1)
- Vitamin B6
- Vitamin B12
Vitamin C
What they do
Although water-soluble vitamins have many tasks in the body, one of the about important is helping to free the energy found in the food you consume. Others help go along tissues healthy. Here are some examples of how different vitamins help yous maintain health:
- Release energy. Several B vitamins are fundamental components of certain coenzymes (molecules that aid enzymes) that help release energy from food.
- Produce energy. Thiamin, riboflavin, niacin, pantothenic acid, and biotin engage in free energy production.
- Build proteins and cells. Vitamins B6, B12, and folic acid metabolize amino acids (the building blocks of proteins) and help cells multiply.
- Make collagen. One of many roles played by vitamin C is to help make collagen, which knits together wounds, supports blood vessel walls, and forms a base of operations for teeth and bones.
Words to the wise
Reverse to popular conventionalities, some water-soluble vitamins can stay in the body for long periods of time. Yous probably have several years' supply of vitamin B12 in your liver. And even folic acrid and vitamin C stores tin can last more than than a couple of days.
Generally, though, water-soluble vitamins should be replenished every few days.
Just be aware that at that place is a minor risk that consuming big amounts of some of these micronutrients through supplements may exist quite harmful. For example, very high doses of B6—many times the recommended amount of 1.three milligrams (mg) per day for adults—can damage nerves, causing numbness and muscle weakness.
A closer look at fatty-soluble vitamins
Rather than slipping hands into the bloodstream like most water-soluble vitamins, fat-soluble vitamins gain entry to the blood via lymph channels in the intestinal wall (encounter analogy). Many fat-soluble vitamins travel through the body but under escort by proteins that human activity as carriers.
Absorption of fatty-soluble vitamins
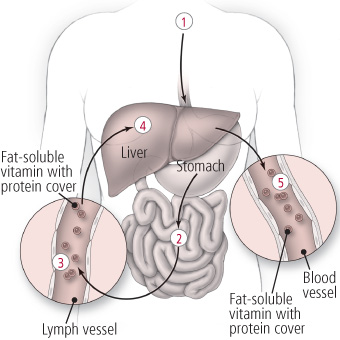
- Food containing fat-soluble vitamins is ingested.
- The food is digested by stomach acrid and and so travels to the minor intestine, where it is digested further. Bile is needed for the assimilation of fatty-soluble vitamins. This substance, which is produced in the liver, flows into the modest intestine, where it breaks down fats. Nutrients are then absorbed through the wall of the small intestine.
- Upon absorption, the fatty-soluble vitamins enter the lymph vessels before making their fashion into the bloodstream. In about cases, fatty-soluble vitamins must be coupled with a protein in order to travel through the body.
- These vitamins are used throughout the body, simply excesses are stored in the liver and fat tissues.
- As additional amounts of these vitamins are needed, your trunk taps into the reserves, releasing them into the bloodstream from the liver.
Fat foods and oils are reservoirs for the iv fat-soluble vitamins. Within your body, fat tissues and the liver act every bit the main holding pens for these vitamins and release them as needed.
To some extent, you can retrieve of these vitamins as time-release micronutrients. Information technology's possible to swallow them every now and over again, perchance in doses weeks or months apart rather than daily, and even so get your fill up. Your trunk squirrels abroad the excess and doles it out gradually to meet your needs.
Fat-soluble vitamins
- Vitamin A
- Vitamin D
- Vitamin E
- Vitamin Grand
What they exercise
Together this vitamin quartet helps keep your eyes, skin, lungs, gastrointestinal tract, and nervous arrangement in skilful repair. Here are some of the other essential roles these vitamins play:
- Build bones. Bone formation would be impossible without vitamins A, D, and K.
- Protect vision. Vitamin A besides helps keep cells healthy and protects your vision.
- Interact favorably. Without vitamin E, your trunk would take difficulty arresting and storing vitamin A.
- Protect the body. Vitamin East also acts as an antioxidant (a chemical compound that helps protect the torso confronting damage from unstable molecules).
Words to the wise
Considering fat-soluble vitamins are stored in your body for long periods, toxic levels can build up. This is nearly likely to happen if you lot take supplements. It'due south very rare to get too much of a vitamin just from food.
A closer look at major minerals
The body needs, and stores, fairly large amounts of the major minerals. These minerals are no more important to your health than the trace minerals; they're but nowadays in your body in greater amounts.
Major minerals travel through the trunk in various ways. Potassium, for example, is quickly absorbed into the bloodstream, where it circulates freely and is excreted by the kidneys, much like a water-soluble vitamin. Calcium is more like a fat-soluble vitamin because information technology requires a carrier for absorption and transport.
Major minerals
- Calcium
- Chloride
- Magnesium
- Phosphorus
- Potassium
- Sodium
- Sulfur
What they do
One of the central tasks of major minerals is to maintain the proper remainder of h2o in the body. Sodium, chloride, and potassium take the pb in doing this. Three other major minerals—calcium, phosphorus, and magnesium—are of import for healthy bones. Sulfur helps stabilize protein structures, including some of those that brand up hair, pare, and nails.
Words to the wise
Having too much of 1 major mineral can result in a deficiency of some other. These sorts of imbalances are usually caused past overloads from supplements, not food sources. Here are 2 examples:
- Common salt overload. Calcium binds with excess sodium in the trunk and is excreted when the body senses that sodium levels must be lowered. That means that if you ingest too much sodium through tabular array salt or processed foods, you could cease upwards losing needed calcium every bit your body rids itself of the surplus sodium.
- Excess phosphorus. Also, too much phosphorus tin can hamper your ability to absorb magnesium.
A closer expect at trace minerals
A thimble could easily contain the distillation of all the trace minerals commonly found in your body. Nonetheless their contributions are just as essential as those of major minerals such equally calcium and phosphorus, which each business relationship for more than a pound of your body weight.
Trace minerals
- Chromium
- Copper
- Fluoride
- Iodine
- Fe
- Manganese
- Molybdenum
- Selenium
- Zinc
What they do
Trace minerals carry out a diverse set of tasks. Here are a few examples:
- Atomic number 26 is all-time known for ferrying oxygen throughout the torso.
- Fluoride strengthens bones and wards off tooth decay.
- Zinc helps blood clot, is essential for taste and smell, and bolsters the immune response.
- Copper helps form several enzymes, i of which assists with iron metabolism and the cosmos of hemoglobin, which carries oxygen in the blood.
The other trace minerals perform as vital jobs, such as helping to block harm to body cells and forming parts of fundamental enzymes or enhancing their activeness.
Words to the wise
Trace minerals interact with one some other, sometimes in means that can trigger imbalances. Too much of 1 can cause or contribute to a deficiency of another. Here are some examples:
- A modest overload of manganese can exacerbate iron deficiency. Having too piffling tin also crusade problems.
- When the body has also trivial iodine, thyroid hormone production slows, causing languor and weight proceeds every bit well as other health concerns. The problem worsens if the body as well has too little selenium.
The difference between "simply plenty" and "too much" of the trace minerals is frequently tiny. Mostly, nutrient is a safe source of trace minerals, but if yous take supplements, it's important to make sure yous're not exceeding rubber levels.
A closer expect at antioxidants
Antioxidant is a catchall term for whatsoever compound that can counteract unstable molecules such as gratis radicals that damage Deoxyribonucleic acid, cell membranes, and other parts of cells.
Your body cells naturally produce plenty of antioxidants to put on patrol. The foods you eat—and, peradventure, some of the supplements you take—are some other source of antioxidant compounds. Carotenoids (such equally lycopene in tomatoes and lutein in kale) and flavonoids (such as anthocyanins in blueberries, quercetin in apples and onions, and catechins in green tea) are antioxidants. The vitamins C and E and the mineral selenium besides have antioxidant properties.
Why free radicals may be harmful
Costless radicals are a natural byproduct of energy metabolism and are too generated by ultraviolet rays, tobacco smoke, and air pollution. They lack a full complement of electrons, which makes them unstable, so they steal electrons from other molecules, damaging those molecules in the process.
Complimentary radicals have a well-deserved reputation for causing cellular damage. But they can be helpful, too. When immune system cells muster to fight intruders, the oxygen they apply spins off an army of costless radicals that destroys viruses, bacteria, and damaged body cells in an oxidative outburst. Vitamin C tin can and so disarm the gratuitous radicals.
How antioxidants may assistance
Antioxidants are able to neutralize marauders such as gratuitous radicals by giving up some of their own electrons. When a vitamin C or Eastward molecule makes this cede, it may allow a crucial poly peptide, cistron, or cell membrane to escape damage. This helps break a concatenation reaction that can affect many other cells.
It is important to recognize that the term "antioxidant" reflects a chemical belongings rather than a specific nutritional property. Each of the nutrients that has antioxidant backdrop as well has numerous other aspects and should exist considered individually. The context is also important—in some settings, for instance, vitamin C is an antioxidant, and in others it can exist a pro-oxidant.
Words to the wise
Articles and advertisements have touted antioxidants as a way to assistance slow aging, fend off heart disease, better flagging vision, and curb cancer. And laboratory studies and many large-scale observational trials (the type that query people about their eating habits and supplement use and and then track their disease patterns) take noted benefits from diets rich in sure antioxidants and, in some cases, from antioxidant supplements.
Merely results from randomized controlled trials (in which people are assigned to accept specific nutrients or a placebo) take failed to back up many of these claims. 1 study that pooled results from 68 randomized trials with over 230,000 participants constitute that people who were given vitamin E, beta carotene, and vitamin A had a higher risk of decease than those who took a placebo. There appeared to exist no effect from vitamin C pills and a pocket-sized reduction in mortality from selenium, but further research on these nutrients is needed.
These findings suggest little overall do good of the antioxidants in pill form. On the other manus, many studies show that people who consume college levels of these antioxidants in nutrient accept a lower risk of many diseases.
The bottom line? Eating a salubrious nutrition is the best way to become your antioxidants.
Source: https://www.helpguide.org/harvard/vitamins-and-minerals.htm
0 Response to "​an Excess of Vitamin _____ Can Result in Hardening of Blood Vessels Due to Excess Blood Calcium."
Post a Comment